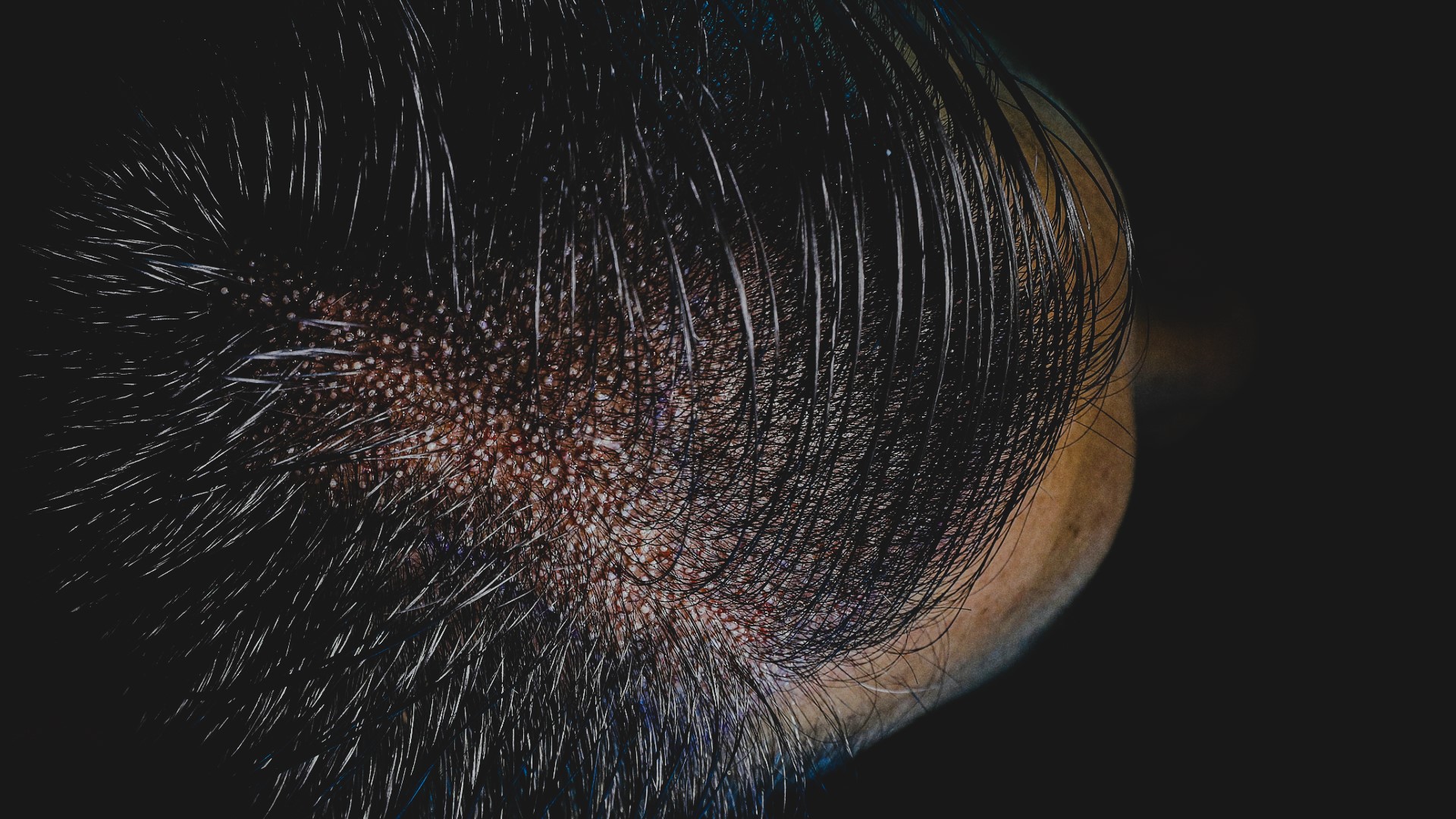
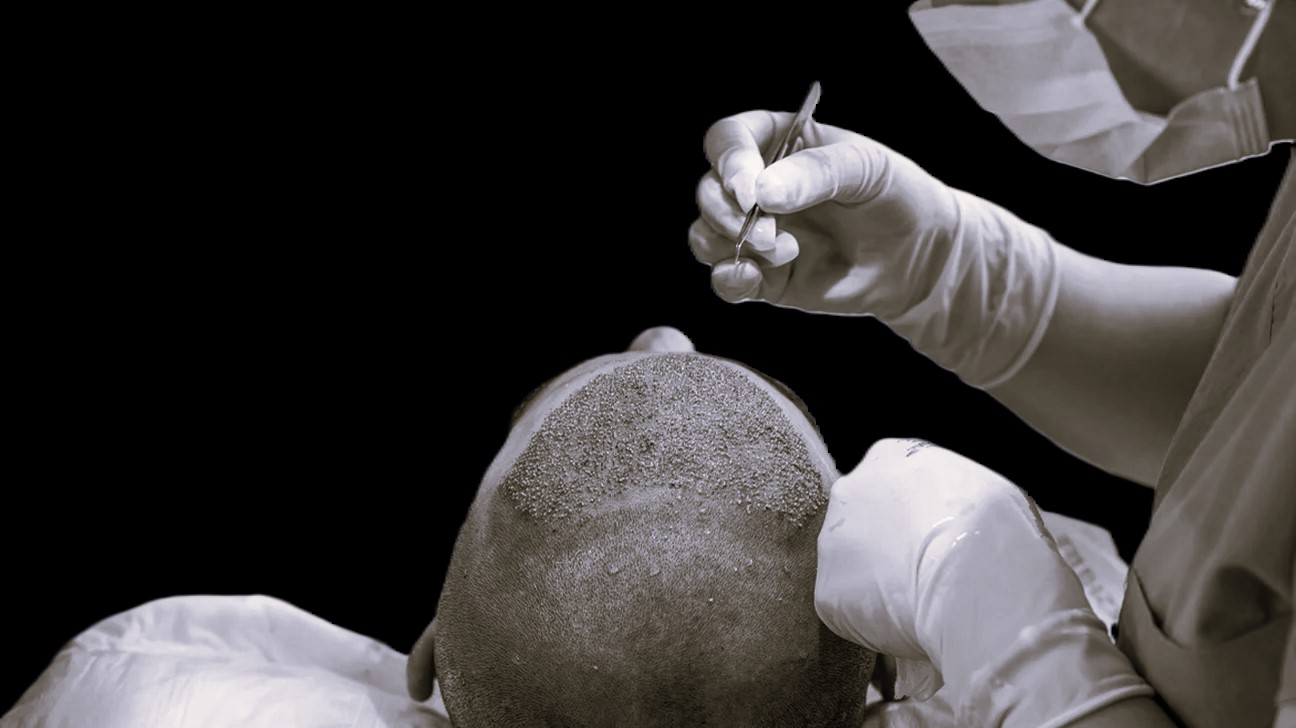
Female's Hair Transplantation
Female hair transplantation has become a topic of great interest in the field of hair restoration treatment. Contrary to common belief, hereditary hair loss can also affect female patients. Unlike male pattern baldness, which typically presents as receding hairline or bald spots on the crown, hair loss in women tends to be more diffuse, with thinning hair spread across the entire scalp.
Thanks to advancements in technology and hair transplantation techniques, the option of hair transplantation and hair restoration for female patients is becoming increasingly popular.

Indications for Hair Transplantation in Females
One of the primary causes of hair loss in women is alopecia. Diagnosis of this type of alopecia can be done through a physical examination using a Trichoscope and a hair loss profile blood test. Multimodality treatments such as cellular therapy and boosting regimens can be effective in managing this condition.
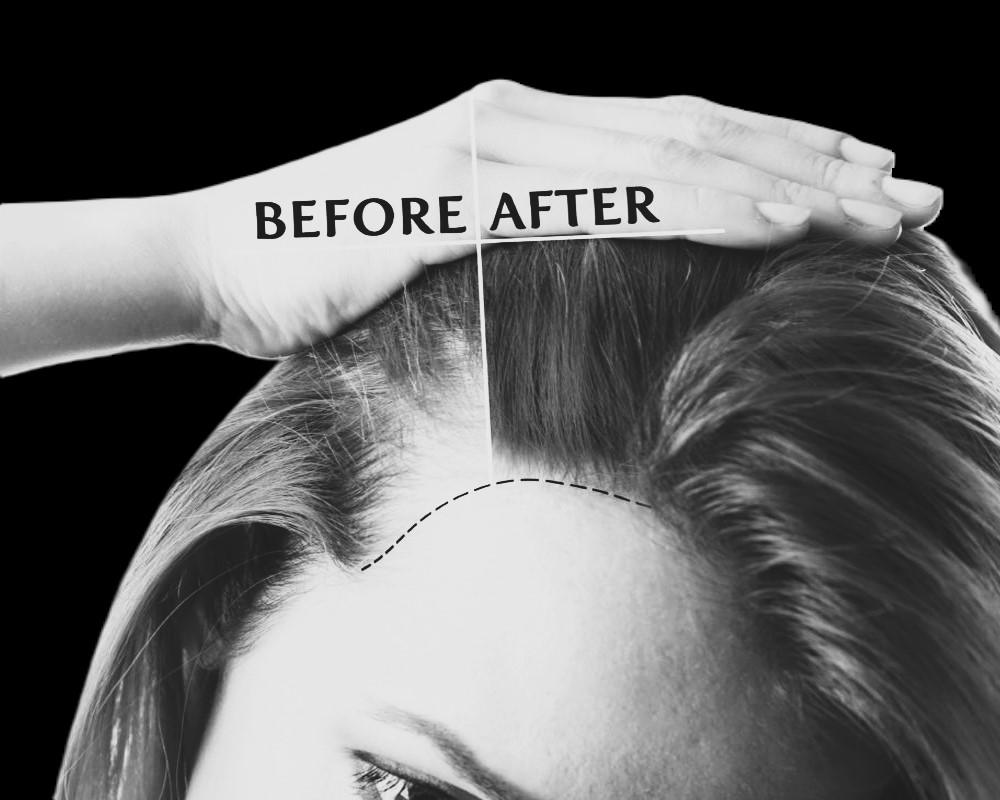
Hair transplantation is typically indicated for female patients with androgenic alopecia. In the initial and intermediate stages, hair loss can potentially be reversed with appropriate hair restoration treatment protocols, leading to a gradual improvement in hair density. However, in the final stages where the follicle is lost, the only viable solution may be female hair transplantation using the Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) technique.
The process of hair transplantation in women is similar to that in men, with some differences in the design of the hairline and the possibility of more grafting in the crown area. At Dr. KARAALTIN Hair Clinic, the cellular boosted follicular graft implantation technique offers significant benefits for hair restoration, particularly in the crown area where female patients often experience significant hair loss.
Before proceeding with a female hair transplant, doctors may struggle to pinpoint a specific cause of hair loss. Alongside genetic factors and aging, there are various reasons behind hair loss in women.
The classification of hair loss in women includes:
1. Alopecia Areata:
Alopecia areata is a condition that leads to hair loss in large patches due to the body's immune system mistakenly attacking healthy hair follicles. In most cases, the damage is temporary, with hair typically regrowing within six months to a year. In rare instances, some women may experience complete hair loss on their scalp and body.
2. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome:
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome often have a hormonal imbalance, resulting in an excess of male hormones. This imbalance can lead to increased facial and body hair growth while causing thinning of scalp hair. Other symptoms may include ovulation issues, acne, and weight gain, although hair thinning may be the only noticeable sign.
3. Ringworm:
Ringworm fungus attacking the scalp can cause distinctive patterns of hair loss, characterized by itchy, rounded bald patches that may be scaly and red. Treatment for ringworm involves antifungal medications, rather than female hair transplantation. It is crucial to identify and treat the infection promptly, as it can spread through direct contact.
4. Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
A deficiency in vitamin B12 can result in fatigue and lack of energy, as well as hair loss issues in women. Vitamin B12 is crucial for the health of red blood cells that transport oxygen to tissues. This deficiency is more common in vegans, as B12 is primarily found in animal products.
5. Pregnancy:
During pregnancy, elevated hormone levels may give the appearance of fuller hair. However, after childbirth, hormonal changes can lead to rapid hair shedding. It may take up to two years for hair to fully recover and return to its pre-pregnancy state.